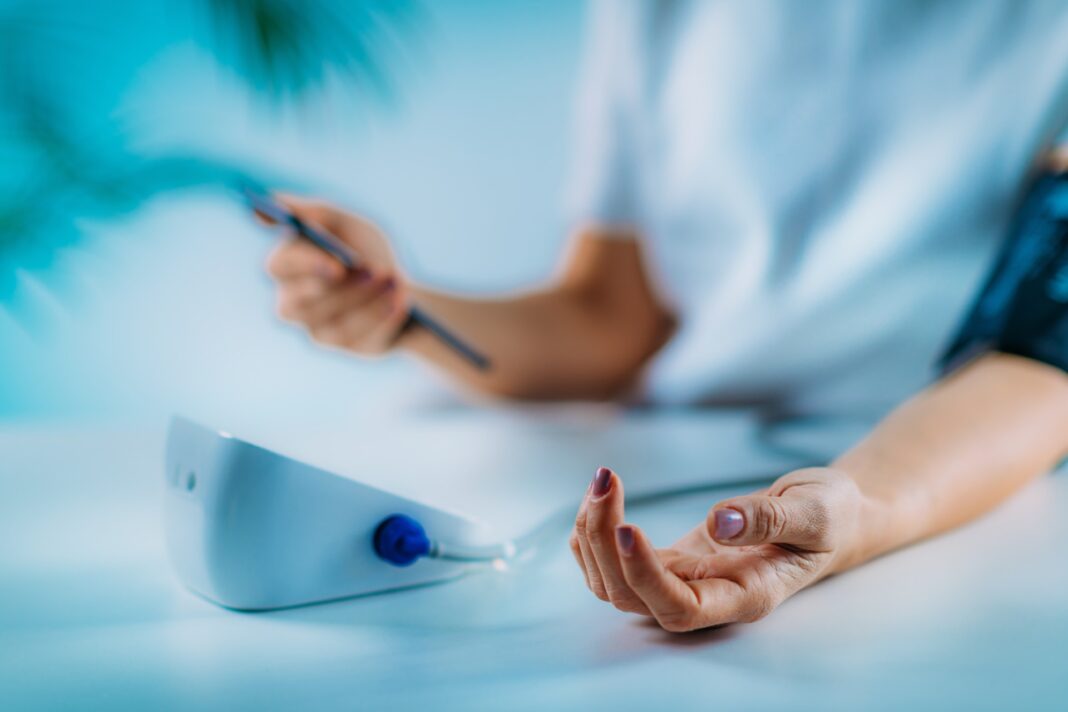
Cleveland. — An innovative study led by Cleveland Clinic revealed that the use of artificial intelligence (AI) combined with precision training can transform the management of type 2 diabetes, achieving more effective glycemic control and reducing the need for medication.
The results, published in the New England Journal of Medicine Catalyst, showed that 71% of the patients who participated in the intervention reached A1C levels below 6.5% using only metformin, the most common standard medication, compared to only 2.4% in the group that received conventional care. The clinical trial was led by Dr. Kevin M. Pantalone, director of Diabetes Initiatives at Cleveland Clinic and professor at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, in collaboration with 13 primary care physicians from the institution. 150 patients were recruited, of whom 100 received the technological intervention and 50 standard treatment.An Innovative Intervention: Twin Precision Treatment
The system, developed by the company Twin Health, combines real-time health metric monitoring — glucose levels, weight, blood pressure, physical activity, and sleep — with guidance from human coaches through a mobile application. The AI generates personalized nutritional and exercise recommendations based on each patient's unique metabolic profile, even predicting the glycemic response to specific meals. Dr. Pantalone emphasized that, unlike the traditional "one-size-fits-all" approach, this strategy allows patients to make more informed and impactful lifestyle decisions:"With the right tools, we can not only control type 2 diabetes more effectively, but also reduce dependence on glucose-lowering medications," he explained.
You can also read: Cleveland Clinic: AI and precision training improve results in type 2 diabetes
In addition to glycemic improvement, participants in the intervention group lost an average of 8.6% of their weight, compared to 4.6% in the control group. A significant reduction in the use of more expensive and complex drugs was also observed, including:- GLP-1 receptor agonists: from 41% to 6%
- SGLT-2 inhibitors: from 27% to 1%
- DPP-4 inhibitors: from 33% to 3%
- Insulin: from 24% to 13%
Implications for Public Health
Type 2 diabetes affects 90% of the nearly 40 million Americans diagnosed with diabetes, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Insufficient control of the disease increases the risk of serious complications such as heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. This study demonstrates that the combination of wearable sensors, AI, and human support could represent a paradigm shift in diabetes management, particularly in primary care. Dr. Pantalone underscored the importance of collaboration between doctors and patients in this breakthrough:“Trusting relationships between primary care physicians and their patients were key to identifying and involving participants. Clinical research starts in the consultation, where meaningful conversations can transform lives”.

 Spanish
Spanish