World War II was a global military conflict that took place between 1939 and 1945. It was the largest war in the history of mankind, with over one hundred million soldiers mobilized and a state of total war in which the major contenders devoted all their economic, military and scientific capacity to the service of the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources.
The opposing sides were: The Allies, which included the United States (Roosevelt/Truman), the United Kingdom (Winston Churchill), the USSR (Iosif Stalin), and France. And on the other side, the Axis with Germany (Adolf Hitler), Italy (Benito Mussolini), and Japan (Hirohito).
Among the causes of the conflict are the failure of the League of Nations, the Treaty of Versailles (1919) which imposed harsh conditions on Germany and the Nazi and fascist expansion: Germany, Italy and Japan sought territories.
Marked by events of enormous repercussions that included the mass death of civilians (the Holocaust, the mass bombings of cities and the use, for the first time in a war conflict, of nuclear weapons), World War II was the deadliest in history, with a result of between 50 and 70 million victims, 2.5% of the world population at that time.

The beginning of the conflict is usually placed on September 1, 1939, with the German invasion of Poland, when the dictator Adolf Hitler decided to incorporate one of his most delicate expansionist claims: The Polish Corridor, which involved the invasion of the western half of Poland; the eastern half, along with Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, was occupied by the Soviet Union.
In response, the United Kingdom and France declared war on him. In the early years, Germany conquered a large part of Europe. Japan, for its part, advanced in Asia and the Pacific.
In 1941, Germany invaded the Soviet Union, and Japan attacked the US base at Pearl Harbor, which led to the entry of the United States into the war. The war became truly global.
Impact on America
Latin American countries declared themselves neutral at the beginning of the war, which slowly began to reach these shores and impact societies divided in their support for both sides.
The economic crisis of 1929, social transformations, the rise of new leaderships and the interest in the collective defense of the continent shaped the positions that, when the war broke out in 1939, would define the American response to the world conflict.
Many countries in the region benefited economically during the conflict by expanding their trade with the Allied powers, especially selling raw materials and food, although there were also major drops in imports from countries at war, as observed by the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC).
Diplomatic ties with the U.S. were strengthened, which promoted Pan-Americanism. Mexico, Brazil, and others sent troops, especially Brazil (the Brazilian Expeditionary Force in Italy).

The End of World War II
On April 30, while Soviet troops advanced towards the Reich Chancellery, Adolf Hitler committed suicide and on May 7 Germany surrendered to the Western Allies in Reims (France) and on May 9 to the Soviets in Berlin (Germany).
By 1945, Italy had been defeated, Germany was suffering a pincer movement, finding itself trapped on two open fronts and Japan was resisting as best it could in the Pacific. With the death of Hitler, it was the propaganda minister, Joseph Goebbels, who assumed power, but he would soon be overwhelmed and would follow the example of his Führer. On May 7, Karl Dönitz (last leader of Nazi Germany) officially surrendered to the Americans.
History records that on August 15, 1945 Japan announced its surrender (Victory over Japan Day, V-J Day) and on September 2, 1945 after the atomic bombs were dropped by the United States on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan officially signed the surrender aboard the battleship USS Missouri.
The Allies won World War II.
United States, Soviet Union (USSR), United Kingdom, France, and China, waved the victory flag that lasted 6 years.
You may be interested in: Putin and Trump congratulated each other on Victory Day through their advisors
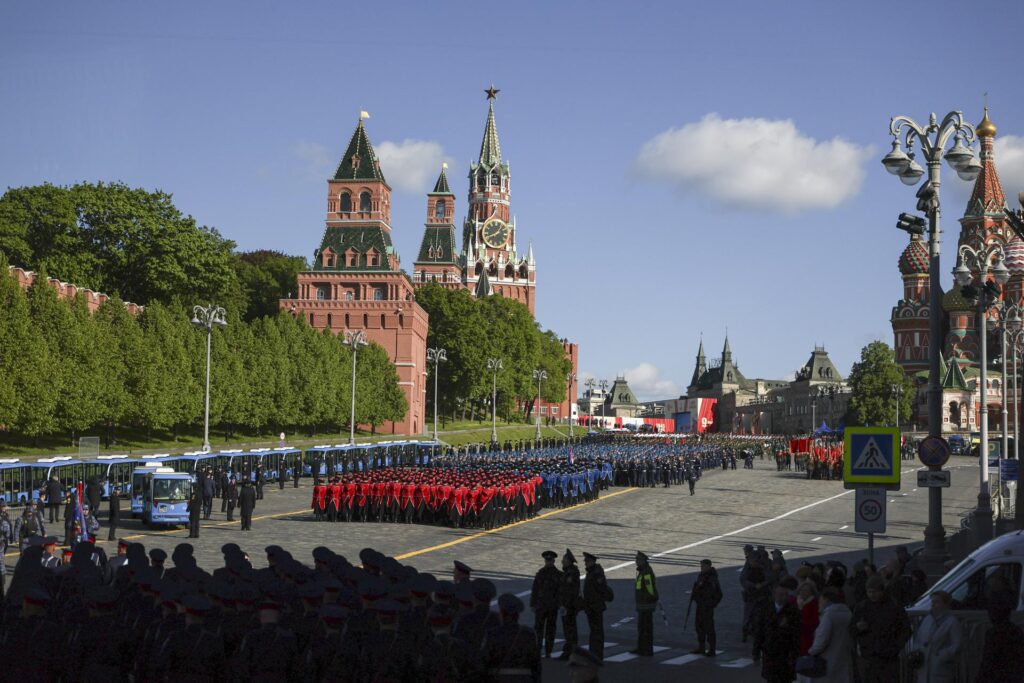

To remember the date, the Victory Day is commemorated, a public holiday in Russia, Belarus and most of the former Soviet republics. In the case of Russia, military parades continue to be held in front of the Kremlin.
The war became a topic of great importance in cinema, literature, history lessons in school, in the media and in the arts. The ritual of celebration gradually obtained a distinctive character with a series of similar elements: ceremonial meetings, speeches, conferences, receptions and fireworks.
Consequences
- More than 60 million dead.
- Holocaust: the genocide of six million Jews.
- Emergence of the U.S. and the USSR as superpowers.
- Start of the Cold War - a period of political, ideological, and military tension between the United States and the Soviet Union, which lasted from 1947 to 1991.
- Foundation of the The United Nations Organization (UN) to prevent future wars.

 Spanish
Spanish